Introduction to geotextiles and geomembranes
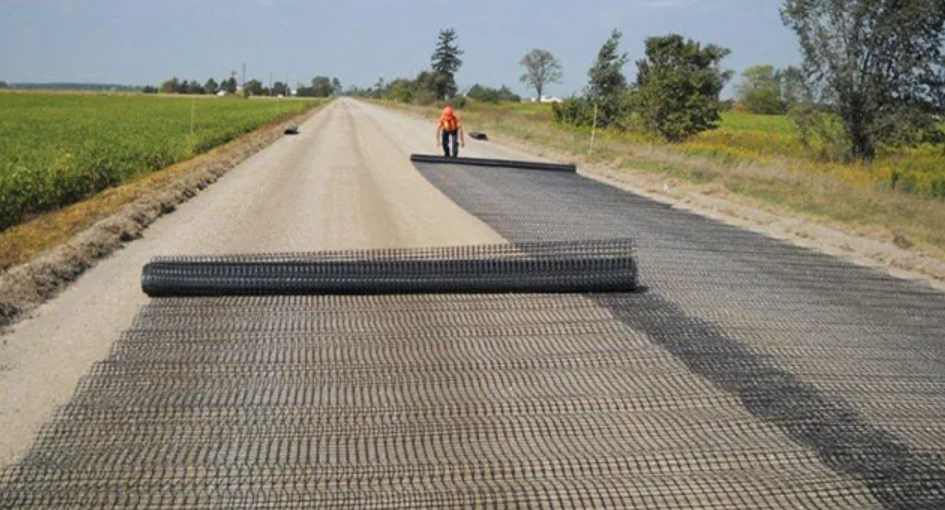
In modern civil engineering, geotextiles and geomembranes are essential materials used to improve soil stability, control erosion, and manage water flow. While geotextiles primarily focus on filtration, separation, and reinforcement, geomembranes provide impermeable barriers for water or chemical containment. Together, they are widely applied in roads, landfills, retaining walls, drainage systems, and environmental protection projects.
Understanding the functions and differences between geotextiles and geomembranes helps engineers select the right materials for long-lasting and sustainable infrastructure.
What Are Geotextiles?
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics made from synthetic fibers such as polypropylene or polyester. They allow water to pass while retaining soil particles and are used for:
- Soil separation
- Filtration of fine particles
- Drainage support
- Erosion control
- Subgrade reinforcement
By performing these functions, geotextiles improve the durability of roads, retaining walls, drainage systems, and other civil engineering projects.
What Are Geomembranes?
Geomembranes are impermeable synthetic liners, typically made from polyethylene or PVC, used to prevent the passage of liquids. Common applications include:
- Landfill liners and covers
- Pond liners and water retention systems
- Containment of chemicals or leachate
- Waterproofing in tunnels or reservoirs
Geomembranes provide a reliable barrier against fluid leakage, complementing the filtration and drainage functions of geotextiles.
See also: How Proper Business Formation Reduces Risk and Unlocks Opportunity
Types of Geotextiles and Geomembranes
Nonwoven Geotextiles
- Produced by needle-punching or thermal bonding fibers
- High permeability and excellent filtration properties
- Ideal for drainage layers, retaining wall backfill, and road base separation
Woven Geotextiles
- Manufactured by interlacing yarns
- Provides high tensile strength and reinforcement
- Suitable for high-stress areas and soil stabilization projects
Geomembranes
- Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), or PVC
- Provides impermeable lining for liquids
- Available in sheets or rolls with varying thicknesses depending on application
Applications of Geotextiles and Geomembranes
Landfills
- Geomembranes serve as impermeable liners to contain leachate
- Geotextiles provide filtration and separation layers beneath or above geomembranes
Road and Highway Construction
- Geotextiles separate subgrade soil from aggregates, reducing settlement and improving pavement stability
- Geomembranes can be used in areas requiring waterproofing or contamination prevention
Retaining Walls and Erosion Control
- Geotextiles filter soil behind retaining walls and under riprap
- Geomembranes prevent water infiltration where impermeability is needed
Environmental Projects
- Geomembranes contain water or chemicals in ponds, reservoirs, or treatment systems
- Geotextiles reinforce soil and protect geomembranes from punctures or damage
Advantages of Using Geotextiles and Geomembranes
- Enhance soil stability and structural integrity
- Provide efficient drainage and filtration
- Prevent fluid leakage and contamination
- Durable and resistant to installation damage
- Support sustainable construction practices
Combining geotextiles and geotextiles and geomembranes creates a multifunctional system that addresses both filtration and containment needs in civil engineering.
Design and Installation Considerations
Material Selection
Choose the appropriate geotextile or geomembrane type based on project requirements, soil conditions, and hydraulic or chemical exposure.
Proper Installation
- Ensure subgrade is leveled and free from sharp objects
- Overlap seams correctly for continuous coverage
- Protect geomembranes with geotextiles to prevent punctures
Maintenance
Inspect and maintain drainage systems and liners regularly to prevent clogging or damage over time.
Contribution to Sustainable Infrastructure
Using geotextiles and geomembranes supports sustainable construction by:
- Reducing soil erosion and sediment loss
- Preventing contamination of water bodies
- Extending infrastructure lifespan
- Minimizing maintenance and repair costs
Conclusion
Geotextiles and geomembranes are complementary materials in civil engineering, providing filtration, separation, drainage, and containment. Their proper selection and installation enhance the stability, safety, and sustainability of roads, landfills, retaining walls, and environmental projects.
By combining the filtration properties of geotextiles with the impermeability of geomembranes, engineers can achieve durable and environmentally responsible infrastructure solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between geotextiles and geomembranes?
Geotextiles are permeable fabrics used for filtration, separation, and reinforcement, while geomembranes are impermeable liners used to prevent fluid leakage.
Can geotextiles and geomembranes be used together?
Yes, geotextiles often protect and support geomembranes, enhancing durability and performance.
How long do geotextiles and geomembranes last?
With proper installation and protection, geotextiles and geomembranes can last several decades.
Are geotextiles and geomembranes environmentally friendly?
Yes, they help control erosion, prevent contamination, and promote sustainable construction practices.
What are common applications of geotextiles and geomembranes?
They are widely used in landfills, roads, retaining walls, drainage systems, ponds, reservoirs, and erosion control projects.